How COVID-19 has changed Korean consumer habits
The COVID-19 pandemic has raised public awareness of hygiene, the environment, and social distancing and subsequently, consumers are increasingly focused on online retail, personal mobility, home appliances/interiors, healthcare and wellbeing sectors.
Social distancing measures, supported by the constantly evolving telecommunication technology have accelerated demand for online retailing making Korea one of the major e-commerce markets in the world. The Korean e-commerce sector has caught the attention of global investors as witnessed by the successful IPO of Coupang Inc on the NYSE – a Korean version of Amazon in the online retailing space with a market cap of c.US$ 72 billion, as of 21 April 2021.
Yeouido Hangang Park, Seoul, Korea
Demand for personal mobility has also grown significantly to reduce human contact. This includes the widespread use of rented electric scooters that also require advanced telecommunication technology.
As people spend more time at home, interest in home activities including cooking, decorating and furnishing has grown significantly.
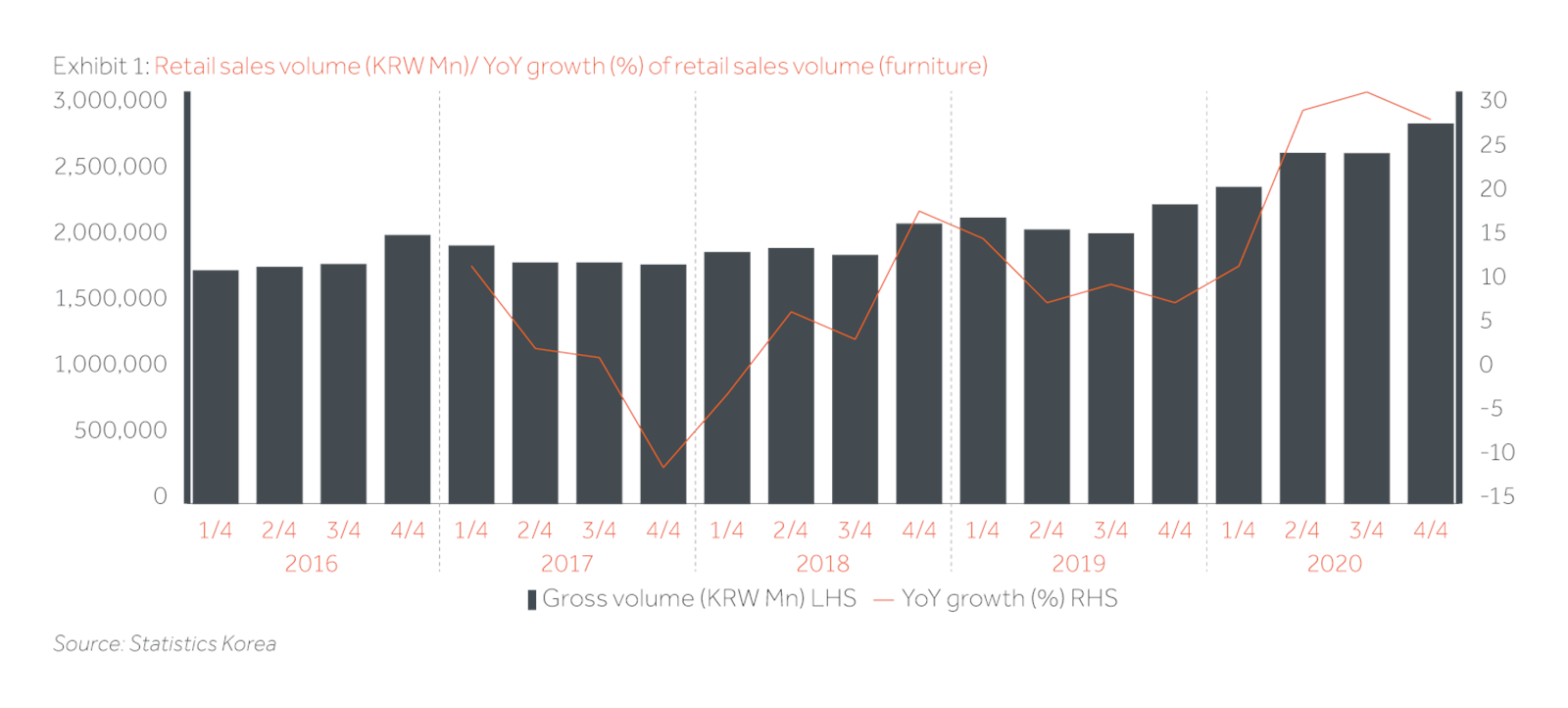
In 2020, Statistics Korea recorded that retail sales volume of furniture reached c.KRW 10.2 trillion, which is a record breaking figure and is a c.24% increase from 2019 and while this has been partly driven by rapid growth of the single-person household accounting for 39% of the total households in Korea as recorded by Ministry of the Interior and Safety (“MOIS”), the on-going pandemic has not only accelerated the growth but was also a major driver in 2020.
Consumers have also shown a strong interest in healthcare including growing demand for health supplements and the so-called “greener” leisure activities for example, weekend farming, mountain hiking, and day trips to the suburbs or rural areas.
Many traditional industries have also been hit by COVID-19 most notably travel and tourism. The Korean Government imposed appropriate measures to limit the spread and both industries and end-users followed such measures well. As a result, domestic travel and tourist activity have remained reasonably resilient.
COVID-19 has accelerated digital transformation across almost every industry driven by advances in telecommunication technology. Starting from e-commerce activities (e.g., online retailing), the digital transformation has continued to significantly upgrade the quality of media content including streaming services and mobile gaming and this upgraded media content has created a huge amount of data traffic.
Korea continues to actively set up the next generation digital infrastructures (5G) across the nation, but it is still in an early stage with a highly limited millimetre wave bandwidth access (26.5~28.9 GHz vs. current 3.4~3.7 GHz) that allows end-users to experience the true performance of the 5G technology.
Nevertheless, even with the current low performing 5G infrastructures, data consumption per capita has already grown significantly and quality data centres that can process and store the rapidly growing data consumption are still not enough.